
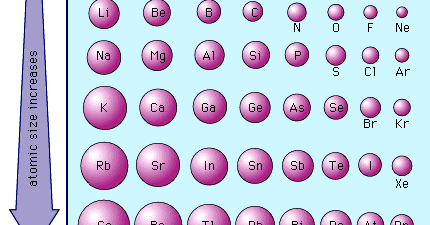
The simple extrapolation of the atomic radius trend for the alkali metals in the graph at left suggests that francium is definitely a contender for largest atom. We can try to predict unknown properties by extrapolating the properties of its 'brothers and sisters' in the same family. How can we predict the atomic radius of francium? The distance between atoms in metallic francium has not yet been measured. It's the least stable of the first 103 elements the most stable Fr isotope has a half-life of just 22 minutes. The answer is "possibly, but we just don't know yet." Francium isn't easy to study. But shouldn't francium, in the next period with an even larger valence shell, be even larger?

The usual periodic trend for atomic size places larger atoms at the left of a row and towards the bottom of a column on the periodic table. Water and even ice reacts more violently with cesium than any of the other common metals: Cesium bursts into flames on contact with oxygen in air. The electron is taken from cesium by other substances in violent chemical reactions. Cesium's lone valence electron is so far away from the nucleus on average that it is very easily removed. Nuclear charge increases going left to right across table rows, so the largest atoms should be found on the left edge of the table.ĭoes having such large atoms make any difference in cesium's properties? Yes.Ĭesium is one of the most reactive elements known, partially because its atoms are so large. A low nuclear charge means that electrons can wander further, on average, from the nucleus. The valence shell (the outer 'peel' of the atom) is largest in atoms at the bottom of the periodic table. Why are cesium atoms so big? Cesium has a large valence shell and a relatively low effective nuclear charge. Rubidium also has large atoms,īut its atomic radius is almost 30 pm less than cesium's. The atomic radius of Cs is given variously as 273.1 pm, 265 pm ,Ģ65.5 pm or 260 pm. What is the largest atom (in terms of volume not atomic mass or weight)?Ĭesium (Cs), tucked in the lower left hand corner of the table, has the largest known atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
